Understanding Psoriasis and Strategies for Management
Psoriasis as an Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Disease
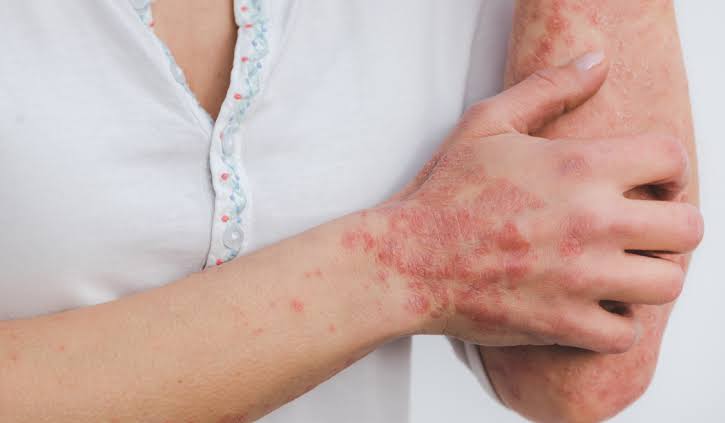
Psoriasis is recognized as an immune-mediated inflammatory disease, although its exact cause remains unknown. This condition is marked by systemic inflammation that primarily affects the skin but can also impact other parts of the body such as the joints and eyes. The prevalence of psoriasis in the United States is notable, with up to 3% of adults affected.
Pathophysiology
In individuals with psoriasis, there is a dysfunction in the immune system that leads to the accumulation of inflammatory cells in the dermis, the middle layer of the skin. This dysfunction accelerates the growth of skin cells in the epidermis, resulting in the formation of raised plaques and scales. Normally, skin cells undergo a cycle of growth and shedding over a month, but in psoriasis, this process is drastically shortened to just a few days. Instead of shedding, the skin cells accumulate, causing the characteristic symptoms of psoriasis: raised plaques, scaling, swelling, and redness or discoloration.
Systemic Effects
Psoriasis is more than just a skin condition; it has systemic implications. The inflammation associated with psoriasis can increase the risk of several serious health conditions, including heart disease, cancer, inflammatory bowel disease, and psoriatic arthritis. This underscores the importance of managing the inflammation effectively to mitigate these risks.
Reducing Inflammation Through Lifestyle and Dietary Changes
Studies suggest that individuals can reduce the inflammation associated with psoriasis through lifestyle and dietary modifications, potentially leading to symptom remission. Key strategies include:
- Dietary Adjustments:
- Avoiding Inflammatory Foods: Reducing intake of pro-inflammatory substances found in soda, ultra-processed foods, salty snacks, sweets, and processed meats.
- Adopting an Anti-Inflammatory Diet: Embracing diets rich in fruits, vegetables, and other nutritious foods. For example, a Mediterranean-style diet has been associated with less severe psoriasis.
- Weight Management:
- Addressing Obesity: Obesity is a risk factor for psoriasis and can exacerbate symptoms. Weight loss has been shown to reduce inflammatory markers and improve psoriasis severity. A 2020 study indicated significant improvements in psoriasis severity following weight loss in overweight or obese individuals.
- Healthy Habits:
- Quitting Smoking: Smoking is detrimental to health and exacerbates inflammatory diseases, including psoriasis.
- Reducing Alcohol Intake: Excessive alcohol consumption can increase inflammation and worsen psoriasis symptoms.
- Increasing Physical Activity: Regular exercise is beneficial, as sedentary lifestyles are linked to more severe psoriasis symptoms.
- Ensuring Adequate Sleep: Poor sleep can increase inflammation. Adults are advised to get 7–9 hours of sleep per night to maintain optimal health.
- Managing Stress: Chronic stress can overactivate the immune system and increase inflammation. Stress-reducing techniques such as meditation and yoga can be helpful.
Medical Treatment Options
In addition to lifestyle changes, certain medications are effective in reducing inflammation and managing psoriasis symptoms. These include topical corticosteroids, injectable biologics, and oral medications. The choice of treatment varies based on the severity of symptoms and individual patient needs.
Personalized Treatment Approach
Each individual with psoriasis may require a tailored treatment plan. Consulting with healthcare professionals, including dermatologists, is crucial for determining the most appropriate treatment methods and lifestyle recommendations. Healthcare providers can also advise on the use of vitamins or supplements to support overall health and manage psoriasis.
Conclusion
Psoriasis is a complex, immune-mediated inflammatory disease that requires a multifaceted approach for management. While medical treatments are essential, lifestyle and dietary changes play a significant role in reducing inflammation and improving quality of life. By adopting healthy habits, individuals with psoriasis can manage their symptoms more effectively and reduce the risk of associated health conditions. For personalized advice and treatment plans, consulting healthcare professionals is recommended.


